Can Sunscreen Cause A Sunburn?

The Bottom Line
We use sunscreens to protect our skin from the sun's harmful rays. In some cases though, the use of sunscreen can result in allergic reactions or photoallergic dermatitis. Fortunately, in most cases, the rash is self-limiting and can be prevented in the future by avoiding use of certain sunscreen products.
The Full Story
Sunlight is essential for the development and survival of life on earth, and includes the visible spectrum and ultraviolet radiation. Exposure to ultraviolet radiation is known to be a primary risk factor for sunburns, skin cancer, and sun-related aging. Ultraviolet radiation is divided into ultraviolet-A (UVA), ultraviolet-B (UVB), and ultraviolet-C (UVC) classifications. Since UVC radiation is filtered out by the ozone layer before it reaches the earth, UVA and UVB radiation are the primary targets of sunscreens and other sun-protection products. UVA radiation is associated with premature aging, while UVB radiation is largely responsible for the development of sunburns and skin cancers.
Currently available sunscreens include physical (inorganic) and chemical (organic) products. Physical sunscreens, including titanium dioxide and zinc oxide, reflect and scatter ultraviolet light from the skin. Chemical sunscreens, including PABA derivatives and benzophenones, absorb and stabilize ultraviolet radiation. Many sunscreens contain combinations of multiple chemical ingredients in order to achieve higher SPF ratings and enhanced water resistance. Chemical sunscreens are also found in cosmetic and personal care products including lipsticks, skin lotions, and hair sprays.
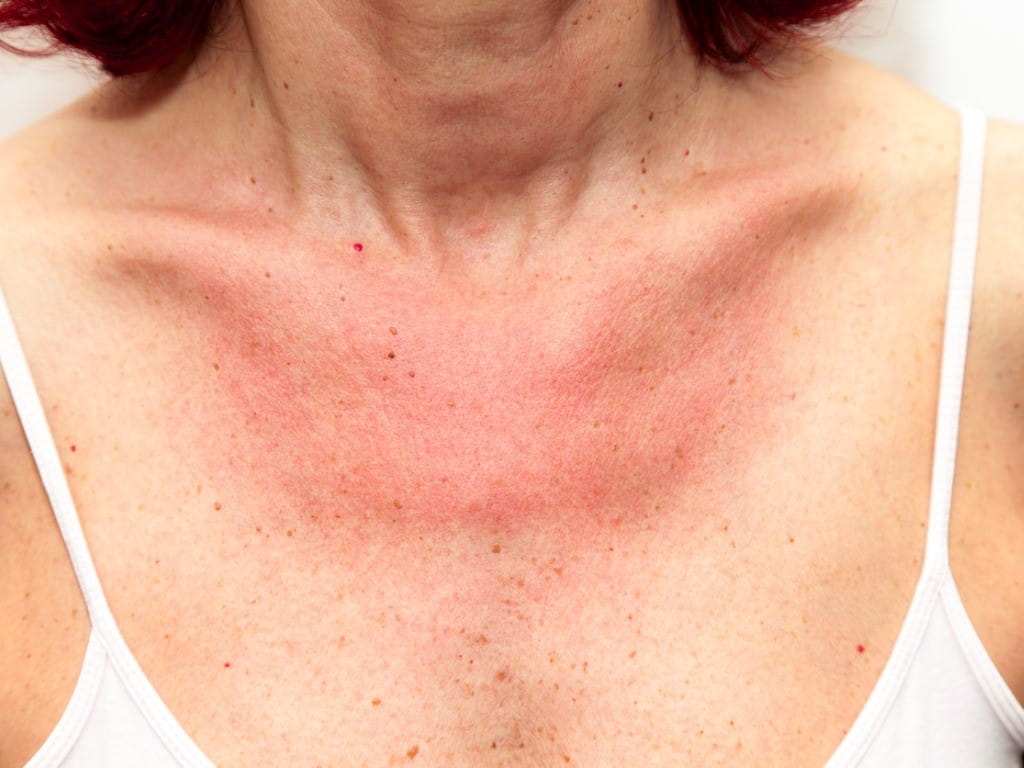
Benzophenone-3, also known as oxybenzone, is the most common benzophenone found in sunscreen products in the United States, and it is well known to cause allergic reactions after skin exposure. Benzophenone-3 (and also other benzophenone derivatives) can cause both allergic contact dermatitis as well as photoallergic dermatitis. Photoallergic dermatitis is a rash that occurs after skin contact with a causative agent (in this case, benzophenone-3 in sunscreen) and UVA radiation. The rash associated with photoallergic dermatitis only occurs in sun-exposed areas including the face, neck, upper chest, legs, and the backs of hands and forearms. Since it only occurs in sun-exposed areas, the rash associated with photoallergic dermatitis may resemble a sunburn. Blistering, itching, or bumpy welts may be present, and the rash may be easily mistaken for a case of poison ivy. The rash generally resolves on its own, but in some cases, it may last for weeks after use of the causative agent. Aside from benzophenones, there are many other topical products that can cause photoallergic dermatitis. Ketoprofen gel, octocrylene (another chemical sunscreen agent), and red tattoo ink have all been reported to cause photoallergic dermatitis.
Treatment of photoallergic dermatitis involves avoiding both the causative agent as well as UVA light until the rash resolves. Topical corticosteroids may be useful for treatment of itching and skin irritation. Patch testing, performed by a dermatologist or allergist, may help identify the triggering causative agents so that they can be avoided in the future.
If you have a question about poisoning or adverse reactions related to use of sunscreens, get help online with the webPOISONCONTROL® tool or call 1-800-222-1222. Both options are free for the public, and available 24 hours a day.
Kelly Johnson-Arbor, MD
Medical Toxicologist
Poisoned?
Call 1-800-222-1222 or
Prevention Tips
- Read sunscreen ingredient labels carefully, especially if you have a history of skin reactions or rashes after use of sunscreens.
- If you have a history of sunscreen allergy, avoid using sunscreens that contain benzophenones, oxybenzone, or octocrylene.
- To reduce the risk of photoallergic dermatitis, always use a sunscreen product that offers UVA as well as UVB protection (look for the phrase “broad spectrum”) on the product label.
This Really Happened
A 66-year-old man, who had a previous history of sunscreen allergy, developed an itchy rash, swelling, and blistering around his eyes, 12 hours after wearing new swimming goggles in an outdoor pool. Patch testing performed by a dermatologist indicated that he was allergic to benzophenone. The swimming goggles were also tested and were found to contain benzophenone, suggesting that this was the cause of the patient’s rash.
References
Heurung AR, Raju SI, Warshaw EM. Benzophenones. Dermatitis. 2014 Jan-Feb;25(1):3-10.
Poisoned?
Call 1-800-222-1222 or
Prevention Tips
- Read sunscreen ingredient labels carefully, especially if you have a history of skin reactions or rashes after use of sunscreens.
- If you have a history of sunscreen allergy, avoid using sunscreens that contain benzophenones, oxybenzone, or octocrylene.
- To reduce the risk of photoallergic dermatitis, always use a sunscreen product that offers UVA as well as UVB protection (look for the phrase “broad spectrum”) on the product label.
This Really Happened
A 66-year-old man, who had a previous history of sunscreen allergy, developed an itchy rash, swelling, and blistering around his eyes, 12 hours after wearing new swimming goggles in an outdoor pool. Patch testing performed by a dermatologist indicated that he was allergic to benzophenone. The swimming goggles were also tested and were found to contain benzophenone, suggesting that this was the cause of the patient’s rash.
